Removing URLs from monitoring
When monitoring a website, ContentKing is able to find and index URLs based on many different types of relations such as incoming links or the sitemap reference. More about how ContentKing finds URLs here: URL finding.
Once ContentKing finds and indexes a URL, it keeps being monitored. ContentKing doesn’t automatically remove URLs from its index even if the content of the pages gets removed, if the page starts returning a 404 or the URL has no incoming relations anymore.
However, there are two ways in which you can remove URLs from ContentKing’s index:
- the URL Exclusion List feature
- the Purge orphan pages feature
URL Exclusion List
The URL Exclusion List feature allows you to exclude certain parts of the website from ContentKing’s monitoring based on URL patterns and essentially works as a virtual robots.txt file for ContentKing.
The URL Exclusion List is very powerful and lets you disallow practically any files and pages apart from the robots.txt file, sitemaps which can be found in the default locations: /sitemap.xml and /sitemap_index.xml and the homepage.
ContentKing does not follow the directives in the actual robots.txt file to be able to access the whole website and report the indexability and relations data accurately.
However, you can easily import the directives from your robots.txt file to the URL Exclusion List in ContentKing.
Setting up the URL Exclusion List
To access the URL Exclusion List go to the website's Settings. At the left side of the screen, click on Set up URL Exclusion List.
There are two steps of setting up the URL Exclusion List:
- Importing directives from the robots.txt file to the URL Exclusion List
- Adding custom exclusion rules
1. Importing directives from the robots.txt file to the URL Exclusion List
After clicking the Set up URL Exclusion List button, as the first step you can import the directives from the website’s robots.txt file (if there is one) to the URL Exclusion List.
Use this step to select which directives (if any) you want to import to the URL Exclusion List:
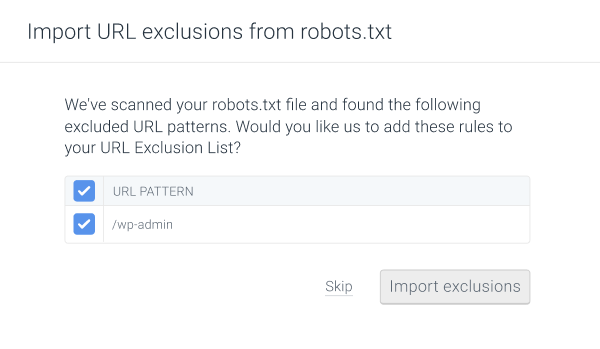
Once you select the directives you want to import, click Import exclusions. If you don’t want to import any directives from the robots.txt file, click Skip.
2. Adding custom exclusion rules
As the next step, you can also add your own URL patterns to exclude from monitoring. If you have imported existing robots.txt directives, they are shown here as well.
The URL Exclusion List follows the robots.txt format (opens in a new tab) and supports both Disallow and Allow directives. The order of the directives doesn’t matter in the URL Exclusion list.
When adding rules to the URL Exclusion List, the Disallow directive is added to the patterns by default.
This means that to exclude a certain URL pattern from monitoring, you can just enter the actual pattern to the URL Exclusion List.
Here are a few common example use cases for custom exclusion rules that can be useful for you:
- An asterisk
*matches any character. -
/admin/excludes all URLs starting with/admin/ -
*?filter=excludes all URLs containing?filter=
If you want ContentKing to monitor a specific subdirectory of the website you can do so using the Allow directive.
The Allow directive is used to override the Disallow directive and allows ContentKing to monitor specific paths within excluded subdirectories:
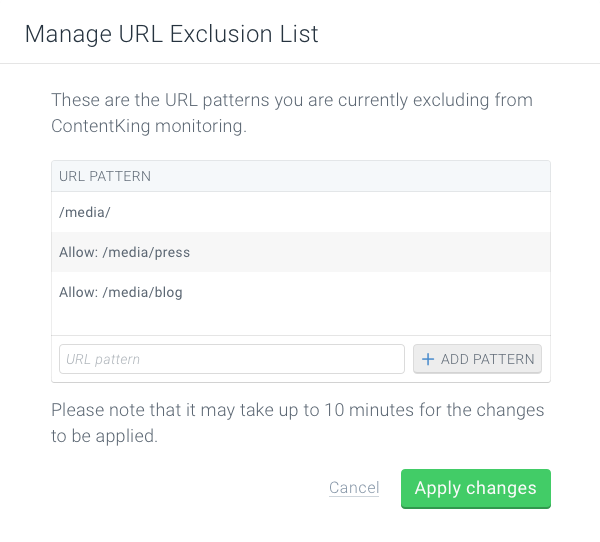
/media/
Allow: /media/press
Allow: /media/blog
The example above excludes the /media/ subdirectory except for /media/press and /media/blog.
Once everything is set up as you wish, click on Apply changes. The exclusions rules will take effect within the next few minutes:
- All monitored URLs matching the exclusion rules will be immediately removed from ContentKing’s index.
- ContentKing will not crawl the URLs matching the pattern at all, unless you remove the exclusion rule from the URL Exclusion List
Purging orphan pages
The Purge orphan pages feature removes all URLs without any incoming relations from ContentKing's index.
This feature is useful for example when you have removed certain pages from your website and their URLs are not being linked within the website anymore.
If you don't want or need ContentKing to monitor such orphaned URLs anymore, you can use this feature to remove them from ContentKing's index.
What is an orphaned page
A URL is considered orphaned in ContentKing if:
- it doesn't have any incoming links
- it doesn't have any incoming redirects
- it doesn't have any incoming canonicals
- it isn't referenced in the XML sitemap
If a URL has any incoming relations pointing to it or is referenced in an XML sitemap it is not considered orphaned and the Purge orphan pages feature doesn’t apply to it.
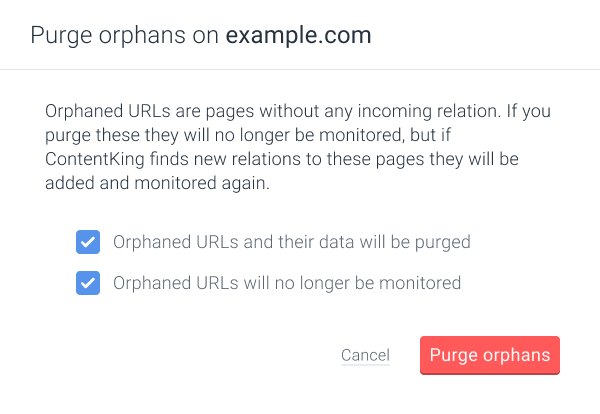
Using the Purge orphaned pages feature
To purge orphaned pages go to the website’s Settings. At the left side of the screen, click on Purge orphan pages.
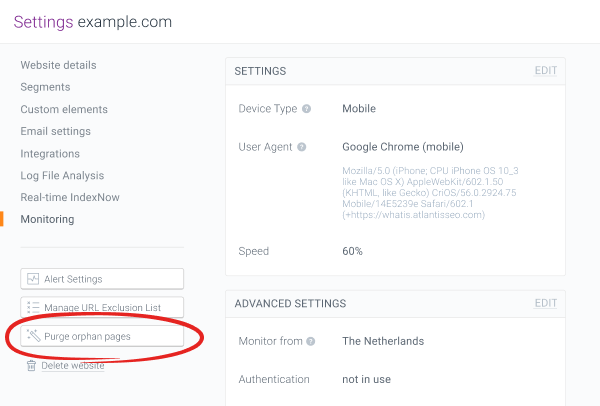
In the next step a pop-up window will appear. Here you need to tick both of the boxes to confirm that you are aware that orphaned URLs will be purged and not monitored anymore by ContentKing.
Once that’s done click Purge orphans.
Need help?
If you have any questions about these features or you need a hand setting them up, don’t hesitate to contact us and we will be happy to help!