What does crawl-delay: 10 mean in robots.txt?
The crawl-delay directive is an unofficial directive meant to communicate to crawlers to slow down crrawling in order not to overload the web server.
Some search engines don't support the crawl-delay directive, and the way the crawl-delay directive is interpreted varies across search engines.
How does Google interpret crawl-delay: 10?
Google doesn't support the crawl-delay directive, so her crawlers will just ignore it.
If you want to ask Google to crawl slower, you need to set the Crawl rate in Google Search Console:
Setting crawl rate in GSC
- Log onto the old Google Search Console .
- Choose the website you want to define the crawl rate for.
- There's only one setting you can tweak:
Crawl rate, with a slider where you can set the preferred crawl rate. By default the crawl rate is set to "Let Google optimize for my site (recommended)".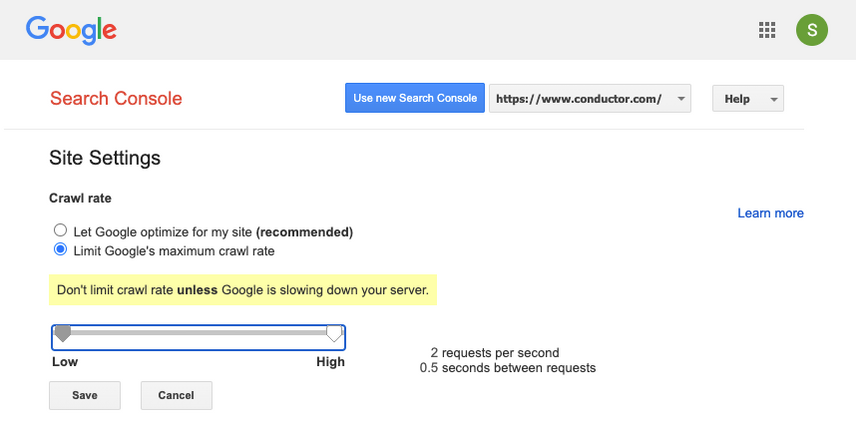
Bing and Yahoo and crawl-delay: 10
Bing and Yahoo support the crawl-delay directive, and in case of crawl-delay: 10 they'll divide a day into 10 second windows and within each window they'll crawl a maximum of one page.
Yandex and crawl-delay: 10
Yandex supports the crawl-delay directive, and in case of crawl-delay: 10 they'll wait a minimum of 10 seconds before requesting another URL.
While Yandex supports this directive, they recommend using Yandex.Webmaster — their version of Google Search Console to define the crawl speed settings .
Baidu and crawl-delay: 10
Baidu does not support the crawl-delay directive, so — similar to Google — they'll ignore the crawl-delay directive. You can define your prefered crawl frequency through Baidu Webmaster Tools.



